Gum Infection Treatment: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Solutions
Gum Infection Treatment: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Solutions
Gum infections, also known as periodontal infections, are a common oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. If left untreated, gum infections can lead to more severe oral health complications, including tooth loss and damage to the surrounding tissues. In this blog, we will explore everything you need to know about gum infections – from symptoms to causes, and effective treatments. By understanding these aspects, you can take the necessary steps to protect your oral health.
What is a Gum Infection?
A gum infection, or periodontal disease, is a condition where the tissues surrounding the teeth become inflamed due to bacterial buildup. This inflammation often starts as mild gingivitis and can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form that affects the bones supporting the teeth.
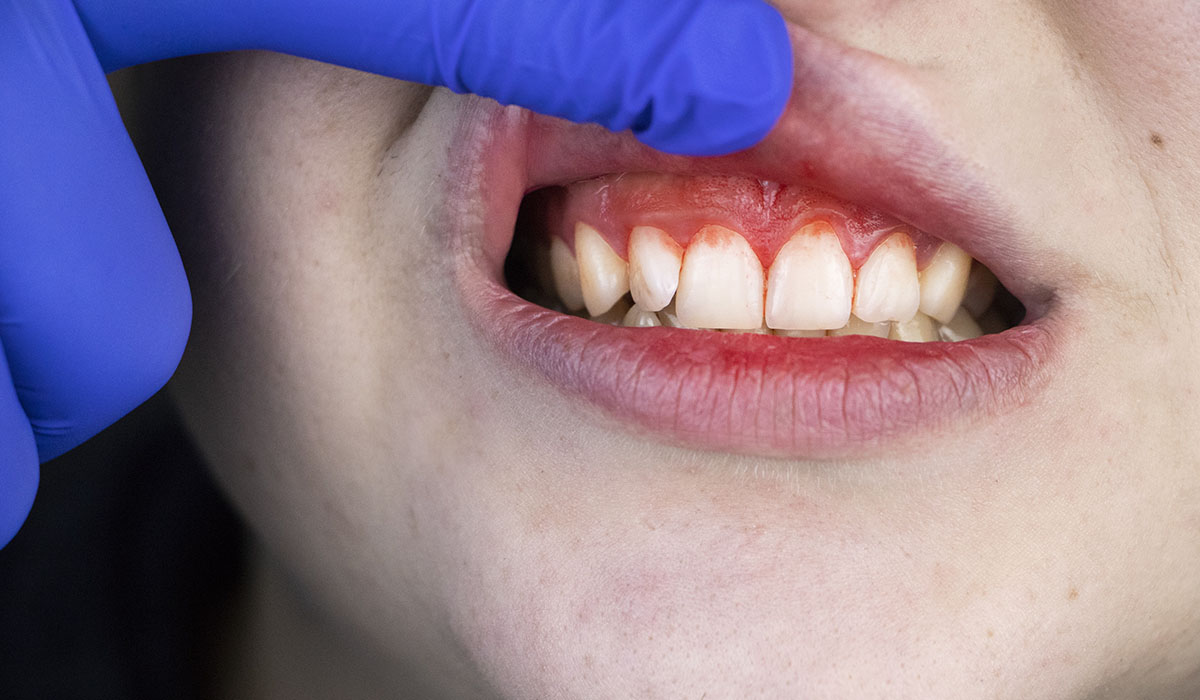
Symptoms of Gum Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of gum infection early can help prevent complications. Common signs include:
- Bleeding gums – When brushing or flossing, you may notice blood, which is a clear sign of inflammation.
- Red, swollen gums – Inflamed gums are often redder than usual and may feel tender.
- Persistent bad breath – Bad breath that doesn’t go away, even with regular oral hygiene, can indicate infection.
- Gum recession – When gums pull away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth root.
- Pain or discomfort – Sensitivity and discomfort around the gums and teeth, especially when chewing or touching the area.
Causes of Gum Infection
Understanding the causes behind gum infections is essential for preventing them. Here are the most common factors:
- Poor oral hygiene – Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate, leading to bacterial growth.
- Bacterial plaque – The sticky film of bacteria on teeth can harden into tartar, which contributes to gum infections.
- Tobacco use – Smoking and using other tobacco products increase the risk of gum infections by impairing the body’s immune response.
- Chronic illnesses – Conditions such as diabetes can weaken the immune system, making gums more susceptible to infections.
- Hormonal changes – Fluctuations in hormones, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can lead to increased sensitivity in the gums.
- Genetics – Some people are more prone to gum infections due to genetic factors.
How Gum Infections Develop
Gum infections typically develop in stages. It starts with mild inflammation (gingivitis) due to plaque buildup. If untreated, the inflammation can progress, causing pockets to form between the gums and teeth, where bacteria thrive. Eventually, this leads to periodontitis, where the bones supporting the teeth can begin to break down, and teeth may loosen.
Gum Infection Treatment Options
The good news is that gum infections can be effectively treated, particularly when caught early. Treatment options vary based on the severity of the infection. Below are some common approaches:
- Professional Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
In the early stages, professional cleaning by a dentist or hygienist can remove plaque and tartar buildup from below the gum line. This is often referred to as scaling and root planing.
- Medications
- Antibiotics – In cases where the infection is severe, dentists may prescribe antibiotics to combat the bacterial overgrowth.
- Antiseptic mouth rinses – These can help reduce plaque buildup and manage early gum inflammation.
- Surgical Interventions
For more advanced cases of periodontitis where the infection has damaged the bone and gums, surgical options may be necessary. These can include:
- Flap surgery – The gums are lifted to remove bacteria and smooth the bone surface.
- Bone grafts – In cases where bone loss has occurred, bone grafting can help regenerate lost bone tissue.
- Tissue regeneration – Special techniques using membranes or other materials can encourage the regrowth of healthy gum tissue.
- Improved Oral Hygiene
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is crucial for preventing gum infections. This includes:
- Brushing twice a day – Use fluoride toothpaste and brush gently yet thoroughly.
- Flossing daily – Flossing helps remove food particles and plaque from between teeth.
- Using an antibacterial mouthwash – This can help kill bacteria and reduce plaque buildup.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Quitting smoking – Tobacco use is a major risk factor for gum disease. Stopping can greatly reduce the chances of gum infections.
- Healthy diet – A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can strengthen gums and support overall oral health.
Why Seek Treatment at Nova Dental Hospital?
At Nova Dental Hospital, we understand the impact that gum infections can have on your overall health and well-being. Our team of highly skilled dentists and oral specialists is dedicated to providing comprehensive and personalized care for gum infections. Using advanced diagnostic tools and treatment techniques, we aim to restore oral health and prevent the progression of gum disease.
With state-of-the-art facilities and a patient-centered approach, Nova Dental Hospital ensures that you receive the highest standard of care. Whether you need routine cleaning, medication, or surgical intervention, our experts are here to guide you through every step of your gum infection treatment journey.
Conclusion
Gum infections, though common, can be effectively managed with timely intervention and proper care. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to maintain your oral health. If you suspect you have a gum infection or want to ensure your gums stay healthy, Nova Dental Hospital is the trusted destination for expert dental care. Visit us today and take the first step toward healthier gums and a brighter smile!







